PC Bottleneck Calculator
How To Use PC Bottleneck Calculator
Step 1: Choose your CPU from the dropdown.
Step 2: Select your GPU from the list.
Step 3: Pick your preferred resolution.
Step 4: Click “Check Bottleneck” to analyze performance.
Step 5: View your result to see which part limits your system.

To get best performance fro myour system, its necessary to plan a balanced build and try to identify early whether you’re CPU-bound or GPU-bound. Our CPU bottleneck calculator will help you to quickly get your bottleneck percentage so you know what is slowing down the PC.
For detailed help, see our guide on how to Build a Custom PC. If you’re planning a laptop purchase or comparing mobile performance, our full Laptop Buying Guide explains how CPU and GPU balance also applies to modern laptops, helping you choose the best setup for gaming, study, or creative work.
Easy Input
Just select your CPU and GPU—no complex setup needed. Our calculator analyzes component utilization and give estimate impact on FPS at your selected resolution.
Compatibility Check
Know instantly if your CPU and GPU are a good match, thanks to a simple CPU-bound or GPU-bound indicator that works like a cpu gpu bottleneck calculator, helping you understand which part needs an upgrade first.
Bottleneck Score
The bottleneck percentage score clearly shows how big the issue is and points out the limiting component, similar to using a computer bottleneck checker for upgrade planning.
Upgrade Advice
Find out whether you should upgrade your CPU or GPU for better performance.
Smarter Choices
Avoid wasting money by fixing what matters first like driver updates, close background processes or try dual-channel RAM.
How To Use PC Bottleneck Calculator Video
Understanding the PC Bottleneck Calculator
Our PC bottleneck calculator specially pinpoints whether you’re CPU-bound or GPU-bound, so if you ever felt to check “what’s my bottleneck” during gaming and multitasking, you will get clear answer. Now during my research and testing I felt useful when frame pacing feels uneven or softwares are not smooth as expected, , and you have a quick pc bottleneck checker style tool instead of guessing.
A PC bottleneck calculator pinpoints whether you’re CPU-bound or GPU-bound, so if you’ve ever wondered “what’s my bottleneck” during gaming or heavy multitasking, you’ll get a clear answer. It’s especially useful when frame pacing feels uneven or apps aren’t as smooth as expected.
We designed it to compare your CPU, GPU, and RAM to check thier balance, you can say it is working like CPU-GPU combo calculator that highlights mismatches. Our CPU-GPU bottleneck calculator analyzes utilization patternsand give you a bottleneck percentage which clear intesisty of matter for gamers and PC builders.
The tool uses smart calculations to detect hardware mismatches. It then gives a percentage score that shows how severe the bottleneck is. For deeper validation, many users cross-check with industry-standard benchmarks like UserBenchmark’s CPU vs GPU comparisons, PassMark’s CPU and GPU charts, or stress tests such as 3DMark by UL Benchmarks. Some people also look at the bottleneck calculator userbenchmark comparison to double-check their numbers.

This is great for checking your system’s current performance, planning future upgrades, or spotting a PC build bottleneck before it slows you down. For many users, it also acts as a simple bottleneck checker that shows whether your system is limited by the CPU or GPU. Even laptop users can benefit, since a dedicated laptop bottleneck calculator helps reveal whether mobile CPUs and GPUs are balanced for gaming or productivity.
In-Depth Guide to CPU and GPU Bottlenecks
In simple words, a bottleneck occurs when one component, CPU or GPU, limits the whole system. This mismatch will be visible as low FPS, frame stutter, or overheating, even if other parts are high-end.
Using a cpu bottleneck calculator or GPU-focused tool before upgrading helps you see whether the processor is holding back your graphics card.
Gamers see frame drops; creators see slow renders; multitasking becomes difficult when background processes Using a CPU/GPU bottleneck calculator or computer bottleneck calculator before upgrading helps keep the system balanced.
According to AMD’s explanation of how CPUs and GPUs work together, the GPU often becomes the primary performance driver at higher resolutions (1440p/4K), and pairing it with a weaker CPU can expose system imbalances.


Common Reasons for CPU Bottlenecks
A CPU bottleneck happens when the processor can’t keep up with GPU or multitasking demands. Modern games and apps lean on core count, clock speed, and cache; an older or entry-level CPU becomes the limiting factor and can cause uneven frame pacing.
We found a CPU bottleneck occurs when your processor dont match with your GPU or cant meet the multitasking demands.
As Intel explains in their guide on CPU bottlenecks, modern games and applications demand core count, clock speed, and cache. An older or entry-level CPU can become a primary reason and can cause uneven frame pacing.
🔍 Typical symptoms include:
- If you face Low FPS in games even if you have a powerful GPU.
- If GPU usage is low and CPU usage is HIGH like 90 to 100%
- During playing games or video rendering occur Freezing, stuttering, or irregular frame times
- Irritating delays in opening apps and switching between tasks when alot of background processes active
- Face poor performance in Heavy games simulation software
⚠️ Main causes of CPU bottlenecks:
- Underpowered processor: I found during my research Older or entry-level CPUs cant handle modern day tasks.
- Too few cores/threads: I found that most games and creative tools become more efficient with 6+ cores.
- Low clock speed: With so many years of experience I can say that a slower GHz rate can’t compete with high FPS demands
- Outdated CPU architecture: One thing to embrace modern softwares are created for newer CPUs
- Limited instruction set support: Incompatibility with modern softwares cause bottleneck
- Background apps eating CPU: Antivirus, system updates, and heavy browser usage are big bottlenecks
Ways to Reduce or Fix CPU Bottlenecks
- First of all Upgrade your CPU to modern CPU which have more cores/threads, higher base clock
- Enable multithreading (Hyper-Threading/SMT) if available
- You can Overclock your CPU safely if your motherboard and cooler support it
- Background programs are resources drainage so close them
- One thing which works for me is disabling startup apps that slow down my PC
- Sometimes change in-game graphics settings can also work like shadows, post-processing
- Updating BIOS/chipset and GPU drivers is most crucial part
- Try to Improve cooling to avoid any thermal throttling
- I use dual-channel RAM to reduce latency and improve data flow
💡 Pro Tip: Use a Bottleneck Calculator for Precision
- You can instantly identify whether its CPU or GPU the limiting factor
- We make it simple and easy to understand with a clear bottleneck percentage and 0 to 100 balance score
- This tool also tell you the upgrade suggestions
- One thing which our tool helps you to avoid spending on parts that won’t help
- Using this tool you can build a balanced system that works efficiently and lasts longer
This is a must-have tool for anyone serious about gaming, streaming, 3D work, or video production, and I’ve seen many people rely on it as a trusted bottleneck calculator when they want quick and clear results. Many Pro players use it as a gaming bottleneck calculator to check if their CPU and GPU are delivering smooth FPS before investing in upgrades.
With all that research and findings I must say that this is the complussory have tool for gaming, streaming, 3D work, or video production. Many gamers use our tool as a gaming bottleneck calculator to identify their CPU and GPU are delivering smooth FPS stable frame pacing before they can think about any kind of changes.
Real-world tests from sources like NVIDIA’s GPU optimization guides and community reviews on PC Gamer or Tom’s Hardware’s bottlenecking explanations show how much FPS can differ depending on component balance.
Wondering if these tools really give accurate results? Check out our full breakdown here: Are Bottleneck Calculators Accurate.
Real-World Fixes for Common PC Bottlenecks
During my research I found that many users assume poor performance indicates the whole system is outdated. But in reality, a single mismatched or underperforming componenet is the reason.
This is what our bottleneck calculator PC exactly reveals. A simple bottleneck test identify the main component which you can upgrade with maximum FPS impact.

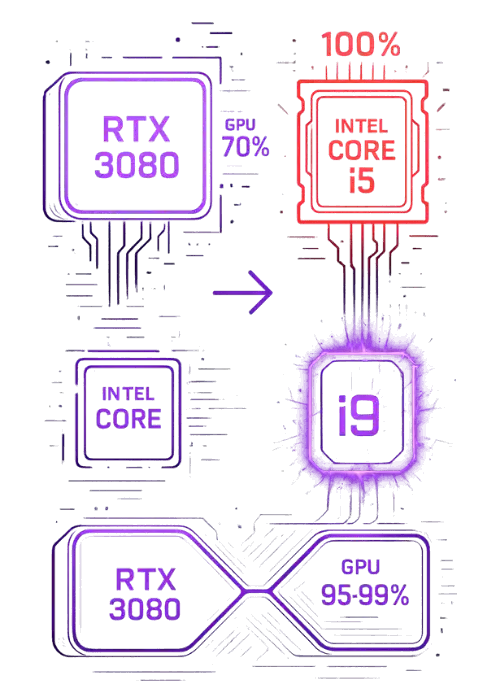
When a High-End GPU Needs a Better CPU
Scenario: A user pairs an RTX 3080 with an older Intel Core i5-7600K. Now in this case despite user have a powerful GPU, but games run at inconsistent frame rates and Powerful GPU never being used at its full potential.
What went wrong:
1. That Old CPU lack cores and threads to compete with modern AAA titles
2. We found it cause frame stuttering and limits the data being sent to the GPU
3. In this case we found CPU usage is at max 100% while GPU usage is low around 60-70%
Smart upgrade: Replacing the i5 with a Core i9-10900K (10 cores, 20 threads) gives full boost to the RTX 3080.
Results:
1. You will see Significant FPS boost in games like Cyberpunk 2077 and Warzone
2. Now there is smooth gameplay with no bottlenecks
3. GPU now performs closer to 95–99% usage consistently
How Upgrading RAM Improves Stability
Scenario: A system with a strong CPU (Ryzen 7 5800X) and a solid GPU (RTX 3060) only has 8GB DDR4 RAM. Games load slowly, multitasking is sluggish, and stuttering happens frequently.
What went wrong:
1. Keep in mind now a days games need more than 8GB ram to run smoothly
2. I must say here Insufficient RAM make your system to rely on slower page file memory
3. No matter you have modern CPU/GPU, they cant compensate for RAM bottlenecks
Smart upgrade: Installing 16GB (2x8GB) DDR4 RAM at 3200MHz gives your system dramatically boosts
Results:
1. Load your games faster and reduce stuttering
2. Allow multitasking like apps, browsers, and games run smoothly at same time
3. System become stable and fast even under heavy workloads


How Better Cooling Can Unlock Full Performance
Scenario: A high-end build with a Ryzen 9 5900X and RTX 4080 struggles under heavy gaming or rendering. Performance dips after 10–15 minutes, and clock speeds drop suddenly.
What went wrong:
1. This particular system is thermal throttling, causing components slow down to avoid overheating
2. This stock cooler can’t handle the heat while working on heavy demanding tasks.
3. At last, poor case airflow traps hot air and won’t allow it to go out, which causes overall system temperature rise.
Smart upgrade: Installing a 240mm AIO liquid cooler and improving case airflow with some additional fans will definitely resolve this heat issue
Results:
1. No more thermal throttling, even under extended loads
2. Consistently higher clock speeds for both CPU and GPU
3. System runs cooler, quieter, and more efficiently
Everything You Should Know to Get Started with Your Bottleneck Results
Understanding your bottleneck calculator results is key to making smart upgrade decisions. Our tool make it simple by providing a bottleneck percentage, which indicates how one component whether CPU or GRU is restricting performance at your target settings.


🔢 What the Percentage Really Means
- The % score tells you the severity of the bottleneck.
- A higher percentage means one component is significantly limiting overall performance.
- The result clearly points out which part—CPU or GPU—is causing the issue.
- For example:
- A 75% CPU bottleneck means your processor is too old or low specs for your graphics card.
- A 65% GPU bottleneck results means your GPU is underpowered with your current system.
🔍 Evaluating Your Components Based on the Score
- If it’s a CPU bottleneck:
- Must upgrade your CPU with the latest and faster processor having cores and threads.
- Consider those models which are optimized for gaming or multitasking
- If it’s a GPU bottleneck:
- Upgrade you old GPU with stronger and latest GPU with more VRAM and align with your resolution/refresh rate (e.g., 1440p/144Hz or 4K/60)
- RAM is also a crucial factor, so double check complete system specs.
Additional Factors That May Lead to PC Bottlenecks
Curious how screen resolution affects bottlenecks? Check out our detailed guide: Can Screen Resolution Cause a PC Bottleneck?
⚠️ Power Supply and Thermal Limitations
- Power Supply Issues:
- Most people ignore wattage because insufficient wattage can stop your GPU and CPU from running at full capacity.
- One of our Poor quality PSUs causes sudden shutdowns and system instability
- One thing which I always check is, proper power connectors which may limit GPU compatibility.
- Thermal Constraints:
- If your system is overheating this may cause thermal throttling, reducing clock speeds
- While building PC consider proper airflow, Poor airflow impact your performance and component lifespan
- Clean your fans regularly, dust in fans or radiators can worsen thermal performance
Solution: Always use the best PSU that meets your wattage needs and ensure proper airflow for effective cooling, also cleans components regularly. Tools like the Seasonic PSU Calculator and the Cooler Master PSU Calculator help you estimate the right wattage before upgrading.


🔄 Storage Type and Speed (HDD vs SSD vs NVMe)
Faster storage doesn’t give you more FPS. But a slow hard drive makes games load longer and can cause little freezes when the game loads new stuff. In our experiment, switching to a fast drive (SSD or NVMe) made levels load much quicker and the whole PC feel snappier.
Storage Peed dont raise FPS directly, but it may cause slow drives increase loading and additionally worsen perceived stutter during asset streaming. Upgrading to SSD or NVMe improves load times and responsiveness.
Solution: One of industry proven thing is upgrade your HDD to SATA SSD or NVMe SSD for faster game loads and smooth multitasking. As Western Digital notes in their SSD vs HDD performance article, SSDs significantly reduce load times, while Samsung highlights the advantages of NVMe drives in high-speed workflows.
🔧 Motherboard Limitations That Affect Performance
- Check PCIe lanes because limited lanes can reduce GPU or SSD performance
- During our experiment we found that weak or outdated VRMs (Voltage Regulator Modules) can limit CPU overclocking or stability
- Motherboard with low ram speed or lack of dual-channel memory
- Missing M.2 slots or Gen 4 support can also restrict SSD performance
- In my tests, old chipsets didn’t support newer features like Resizable BAR, USB 3.2, or Wi-Fi 6.
Now thats why some people now even use a motherboard bottleneck calculator to check board-related slowdowns)
Solution: Use our tool to choose a motherboard that supports your CPU’s full potential. Look for strong VRM design, PCIe Gen 4 or 5 support, and ample expansion slots. Make sure it has proper BIOS support for modern features.

Best Times to Use a Bottleneck Calculator
Our computer bottleneck tester can help you to avoid costly mistakes by showing how yur CPU and GPU are interact in real-world FPS and frame pacing. Whether you’re troubleshooting or planning a new build, it gives you clear insights into how your components work together.
🕹️ When You’re Facing Gaming or Rendering Problems
- If you face sudden frame drop or inconsistent FPS
- If your GPU usage is low but CPU usage shows 100% or vice versa, this calculator tells you which part is lacking so you don’t replace the wrong part.
- If it took too much time in rendering software like Adobe Premiere or Blender
- Face stuttering, lag, or overheating without clear reason
Why use the calculator: The best thing in this calculator is to show exactly which part is lacking behind. So, you can change that specific component without spending too much on changing the wrong part.

🧩 When Planning a New PC Build
- Will this CPU bottleneck the GPU I chose at my target resolution and refresh rate?
- Is my chosen GPU overkill for my processor, or do they have proper cpu gpu compatibility for the performance I want?
- Are my component choices balanced for gaming, editing, or streaming?
Why use the calculator: Why use the calculator: It helps you create a balanced system so your spend translates into real-world performance.
🔄 When You’re Upgrading One Part of Your Setup
- Check whether a new GPU will be CPU-bound on your current platform, confirm PCIe lanes and PSU headroom, and estimate the ROI of the upgrade before you buy.
- See if the new CPU can keep up with your existing GPU
- Ensure your power supply and motherboard still support the upgrade
Why use the calculator: It prevents mismatched upgrades and helps you get the most value out of your investment.

Bottleneck Calculator vs. Manual System Analysis
Use the calculator for a fast CPU-bound/GPU-bound snapshot, then confirm with live monitoring for accuracy before making big purchases. Each method has its strengths, and knowing when to trust the tool versus when to dig deeper manually can make or break your upgrade decisions.
🔍 When Manual Analysis is Better
- You’re already facing real-world performance issues
- You want to analyze RAM, storage, PSU, or thermals
- You need insights per game or software
- You want to monitor live hardware behavior during tasks
🛠️ Tools for Manual Analysis
- MSI Afterburner / RivaTuner for live CPU/GPU monitoring
- HWMonitor to check voltage, power, and thermal readings
- Task Manager / Resource Monitor for usage tracking
- UserBenchMark, Cinebench, 3DMark for stress testing
- CapFrameX this help in frame analysis for gamers
Pro-Level Comparison Table: Bottleneck Calculator vs Manual Analysis
| Feature/Aspect | Bottleneck Calculator | Manual Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Super simple to use, just enter your parts and go | Takes more time and some technical know-how |
| Accuracy | Gives a close idea based on general data | Very accurate since it checks your own system’s behavior |
| Speed of Results | Instant results in a few seconds | Slower because it needs real tests and tracking |
| Components Analyzed | Mainly looks at CPU and GPU | Checks everything like CPU, GPU, RAM, PSU, temperature, and background apps |
| Context Awareness | Doesn’t know which game or app you’re running | Can test how each game or program really performs |
| Live Performance Tracking | No live tracking options | Yes, you can see FPS, usage, and other live stats |
| Thermal and Power Checks | Doesn’t check for heat or power limits | Can show if your system is overheating or losing power |
| Upgrade Planning | Good for basic upgrade advice | Helps find the exact part that needs upgrading |
| Risk of Generalization | Can group hardware by type, not by exact model | Completely based on your real hardware and setup |
| Cost | Usually free and quick to use | Free with tools, but takes more time to do right |
💡 Expert Recommendation
- Use both methods one by one for best results:
- Start with our bottleneck calculator tool to get a quick overview
- Then try manual tools if you’re seeing inconsistent performance.
- With my personal experience I will suggest that gamers, video editors, and power users should always double-check manually before major upgrades
- Manual analysis is also better when comparing real-world performance per game, since calculators don’t simulate software behavior
Best No-Bottleneck PC Builds for 2025
Looking for perfectly balanced PC setups? Here are well our researched, tested and recommended balanced builds, which are tested with our PC bottleneck calculator to ensure minimal bottleneck.
Entry-Level Build
CPU: AMD Ryzen 5 5600
GPU: NVIDIA RTX 4060
Result: ~0% bottleneck
Ideal For: Esports, light AAA gaming, students
Mid-Range Build
CPU: Intel Core i5-13600K
GPU: NVIDIA RTX 4070 Super
Result: ~1–2% bottleneck
Ideal For: Streamers, editors, multitaskers
High-End Build
CPU: AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D
GPU: NVIDIA RTX 4080 Super
Result: ~0% bottleneck
Ideal For: 4K gaming, 3D modeling, VR
Enthusiast Build
CPU: Intel Core i9-14900K
GPU: NVIDIA RTX 4090
Result: ~1% bottleneck (GPU-limited rarely)
Ideal For: Pro gamers, AI/ML devs, creators
💡 Tip
These builds balance core count, GPU power, RAM speed, and cooling. Use them as a base or tweak based on your needs.
Conclusion
Keeping your PC balanced is very important for smooth and fast performance. From my own research and testing, I learned that even one weak part like an old CPU, slow drive, or poor cooling can slow everything down. The PC Bottleneck Calculator helps you quickly find what is causing the slowdown so you can fix it easily. By checking before upgrading, you save money, get higher FPS, and make your computer run better and last longer.

