Understanding CPU Bottlenecking Explained
Last updated:
I’ve seen people get stuck trying to fix a slow computer, but most times, it’s a CPU bottleneck. A CPU bottleneck happens when the processor can’t keep up with other hardware, so your system performance drops.
Imagine a big bottle filled with marbles. The neck of the bottle is small, so only a few marbles get out at once. That neck is the bottleneck. The same thing happens in a PC, if the CPU can’t process data as fast as the GPU or other parts, you get a performance limitation.
I tried running a strong graphics card with an old CPU once. My games stuttered a lot because my CPU bottlenecked the whole system. PC bottlenecks can show up with the CPU, GPU, or any hardware component. That’s why I always check every part when something feels slow especially after reading about the main causes of PC bottlenecks that affect overall performance.
How CPU Bottlenecking Happens in a PC
Every part inside a PC needs to work together, just like a team. The CPU and GPU have to talk fast with each other. The CPU gives the GPU instructions. If the CPU can’t keep up, you get CPU bottlenecking, and the GPU performance drops.
I’ve seen this a lot with friends who put a really good graphics card in a computer with an old CPU. Games feel slow, even when the GPU should be super strong. That’s because the CPU can’t send data to the GPU fast enough.
CPU and GPU Relationship
When I play games, the CPU tells the GPU what to draw. If my CPU gets stuck, the GPU waits. This is a classic CPU bottleneck. The PCIe bus connects these two parts, and if the bus or the CPU is slow, the GPU just sits there waiting. Sometimes, if the CPU is strong but the GPU is weak, you get a GPU bottleneck instead. In that case, the graphics look choppy because the GPU can’t keep up.

Storage Speed
I’ve tried loading big games on a slow SATA drive and on a fast NVMe SSD. The difference is huge. NVMe SSDs use a faster PCIe connection, and that means games load quicker. Storage speed matters because if the storage is slow, even a fast CPU and GPU can’t help. Everything waits for files to load.
RAM Speed and Size
RAM also makes a big difference. If you don’t have enough RAM, or if it’s too slow, your PC will lag. For high-end games, I always use at least 16GB RAM, and I check the RAM speed too. Memory bandwidth, the speed at which RAM moves data, is really important. When I upgraded to faster RAM, my games felt smoother, you can learn more in this detailed guide on RAM bottlenecks and how they affect gaming.
💡 Quick Tip
I use monitoring tools to see what’s maxed out, CPU, GPU, or RAM. If my CPU usage is always at 100% while the GPU isn’t, I know I have a CPU bottlenecking issue. PCIe versions and the number of PCIe lanes also change how fast data moves between hardware parts. The right balance keeps system performance up.
Honestly, every component matters. Even one slow part, CPU, GPU, storage speed, or RAM speed, can limit how well the whole PC works.
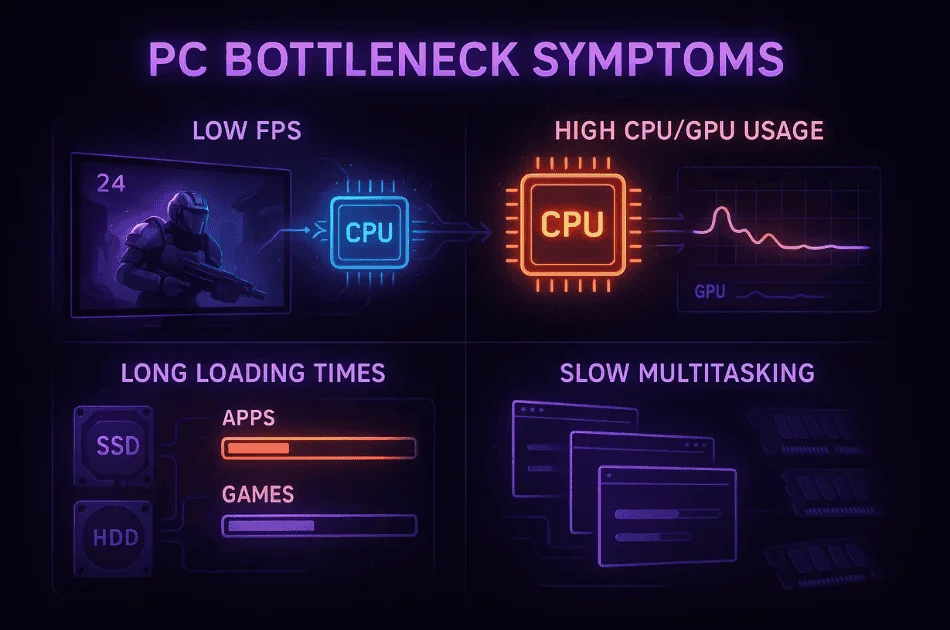
Common Signs of CPU Bottlenecking
I’ve found that knowing the signs of a CPU bottleneck helps me fix performance issues faster. Here’s what I look for:
- Low FPS in games: If I see low FPS even when settings are turned down, it’s usually a CPU bottleneck symptom.
- High CPU or GPU usage stuck at 100%: Sometimes, my CPU runs at full power while the GPU usage stays low, or the other way around. That shows something’s getting held back.
- Long loading times: If my games or apps take forever to load, even with a fast drive, it can point to a bottleneck or slow storage.
- Slow multitasking: When my PC feels sluggish switching between apps, I know multitasking performance issues could be due to RAM limitations or a bottleneck.
I always check usage stats using Task Manager or MSI Afterburner. Free tools like these show me if high CPU utilization or GPU usage is happening. Also, overheating can look just like bottleneck symptoms, so I try to rule out thermal throttling first. It really makes a difference.
How to stop CPU bottlenecking?
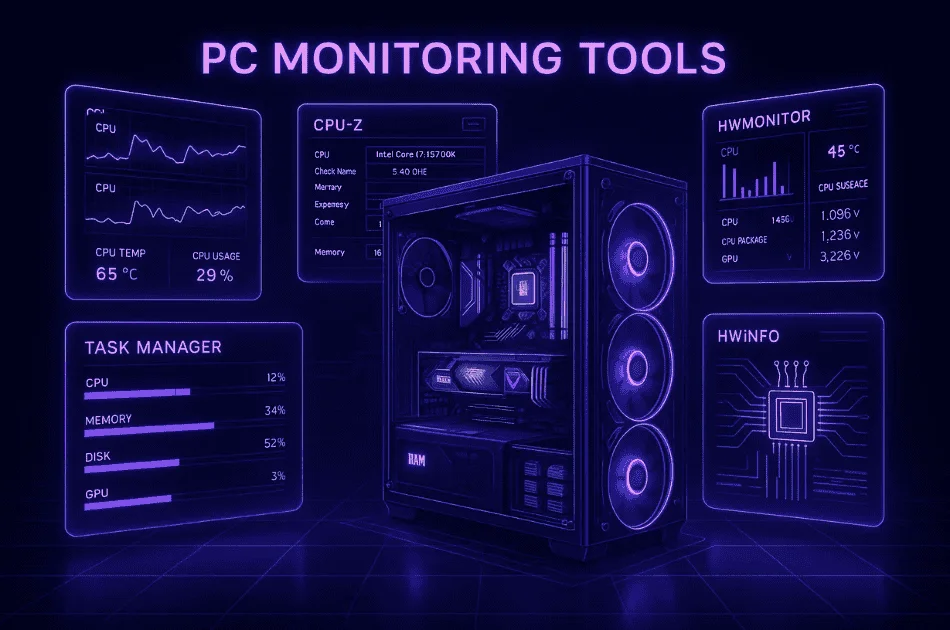
Best Tools to Detect PC Bottlenecks
I use bottleneck detection tools to figure out which part of my PC is slowing things down. These tools show real-time CPU monitoring, GPU monitoring, and more, so I know exactly where the problem is.
- MSI Afterburner: Lets me see CPU/GPU usage and temperatures while I play games.
- CPU-Z: Gives details about my CPU and memory specs, which helps spot limits.
- HWMonitor: Shows hardware health, temps, and voltages, making it easy to find issues.
- Task Manager: This Windows tool tracks resource usage for all my running programs.
- HWiNFO: For more advanced hardware monitoring with deeper info on every component.
I always pair these tools with in-game benchmarks for a better look at how my system is doing under stress. It makes spotting a bottleneck way easier.
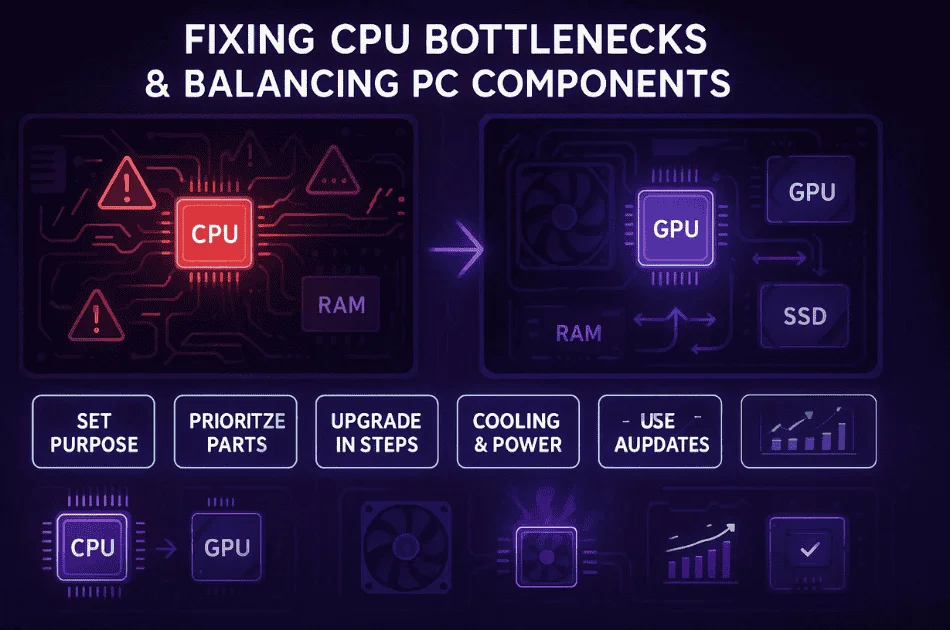
How to Fix or Reduce CPU Bottlenecks
I’ve learned that bottlenecks happen when my PC parts aren’t balanced. If I want smooth performance, I need to fix CPU bottlenecks and avoid mismatched components. Here’s how I do it:
- Set a Clear Purpose: I always decide if my PC is for gaming, video editing, or just office work. That helps me choose the right balance of parts. I also follow this custom PC building guide to plan balanced upgrades and avoid mismatch issues.
- Prioritize Components: If I play games a lot, I focus on the CPU and GPU. For work or editing, I might need more RAM or a better CPU.
- Upgrade in Steps: When I can’t buy everything at once, I upgrade one part at a time. I usually start with the part that limits me most, CPU or GPU. That’s my phased upgrade strategy.
- Check Power Supply and Cooling: Good cooling systems and a strong power supply keep my PC stable. Overheating can slow things down, so I make sure everything stays cool.
- Use Tools and Updates: I use bottleneck calculators and benchmarking tools before I buy new parts. Sometimes, just updating the BIOS or drivers fixes balance problems. But I also make sure to verify results with trusted resources about bottleneck calculator accuracy to avoid wrong upgrade choices.
This way, I keep my components balanced, avoid PC bottlenecks, and enjoy better system performance.
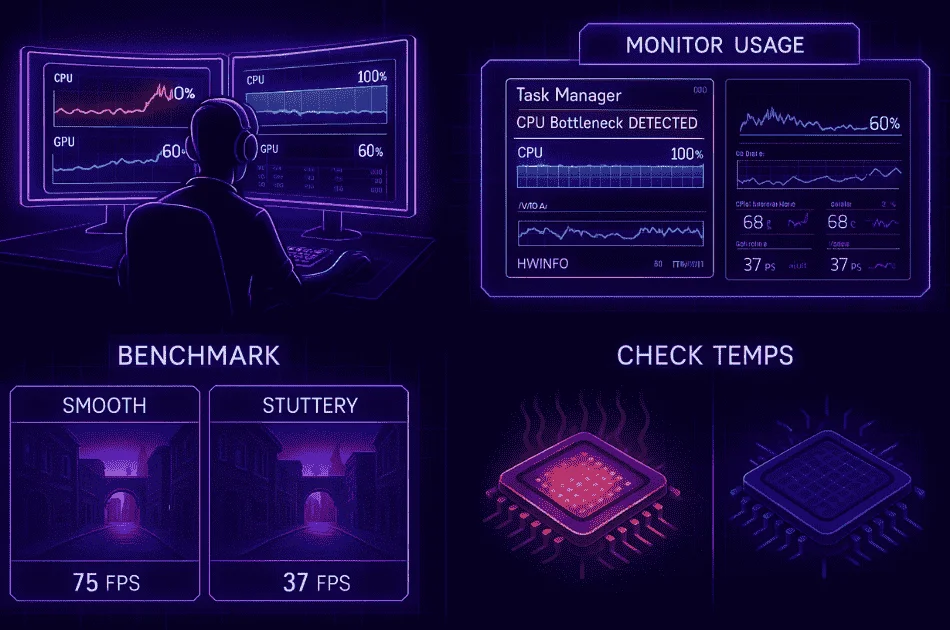
How to Check if Your CPU is Causing a Bottleneck
I always check for CPU bottlenecks when my games feel slow or laggy. Watching CPU usage helps me see if something’s off. Here’s how I do it:
- Open Task Manager: I press Ctrl+Shift+Esc and look at CPU and GPU usage while gaming.
- Spot the Signs: If CPU usage stays close to 100% but GPU usage is much lower, I know I have a CPU bottleneck.
- Use Monitoring Tools: MSI Afterburner and HWMonitor give me real-time stats on how hard my CPU and GPU are working.
- Run In-Game Benchmarks: I run built-in tests in games to compare CPU and GPU performance side by side.
- Check Temps: If my CPU gets too hot, thermal throttling can make it act like a bottleneck, so I keep an eye on temps.
Sometimes, background apps or old drivers give me false results, so I close everything else first. I also try online bottleneck calculators for a quick check. It’s a simple way to spot problems fast.
How to Tell if Your CPU Can Handle Your GPU
Getting the right balance between CPU and GPU is key for smooth gaming performance. If they’re not matched well, I end up with a bottleneck and wasted power. It’s also smart to adjust graphics settings properly to get smoother gameplay and reduce stress on the CPU.
- Check Specifications: I look at CPU cores, clock speed, and see what the manufacturer (Intel or AMD) recommends pairing with my GPU.
- Use Bottleneck Calculators: Tools like PC-Build or PC-Bottleneck show me if my CPU can handle my GPU, or if there’s a weak link.
- Compare In-Game Benchmarks: I always search for real-world tests of my exact CPU-GPU combo. If games run smooth there, it should work for me too.
- Watch Power and Cooling: I make sure my power supply and cooling system are strong enough for both CPU and GPU, or else performance drops.
- Monitor Usage in Real Time: During heavy gaming or tasks, I keep an eye on CPU and GPU usage stats to spot any trouble.
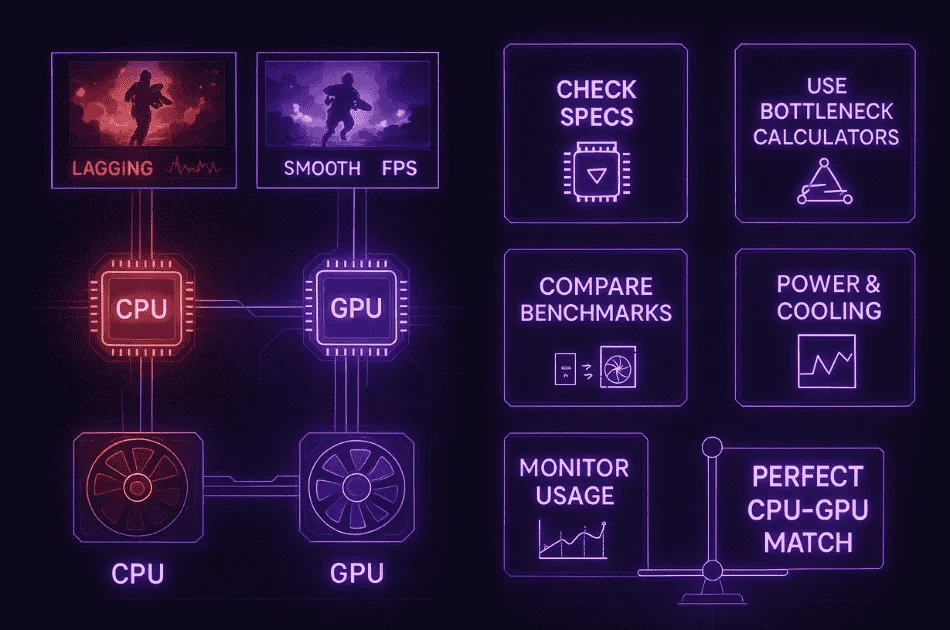
I’ve learned that RAM speed and the motherboard’s PCIe version also change how well my setup works. Even small mismatches can hurt gaming performance, so checking everything matters, especially when understanding how screen resolution can cause PC bottlenecks in demanding games.
Visual Diagrams Showing CPU Bottlenecks in Action
I learn faster with visuals, so here are two simple diagrams that make the idea of a CPU bottleneck clear.
Diagram 1: Normal Data Flow (Balanced System)
Diagram 2: CPU Bottleneck Flow
This PC bottleneck visualization shows how slow CPU vs GPU data flow can hold everything back.
Comparison Table of Common CPU Bottleneck Scenarios
I find tables are a quick way to see when CPU GPU bottlenecks happen and how different setups change PC performance.
| Scenario | CPU | GPU | Result (Bottleneck Type) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-end GPU + Mid CPU | Ryzen 5 3600 | RTX 4090 | CPU bottleneck (30%) | CPU can’t keep up with powerful GPU |
| High-end CPU + Mid GPU | Intel i9-13900K | GTX 1060 | GPU bottleneck (20%) | GPU slows down overall performance |
| Balanced CPU & GPU | Ryzen 7 5800X | RTX 3070 | No major bottleneck | System runs smooth, both parts work well |
| Low-end CPU + High GPU | Pentium G5400 | RTX 3070 | CPU bottleneck (40%) | Big gap, CPU vs GPU performance |
CPU vs GPU performance matters for every build. Even a strong part can’t fix a weak one—balance means better PC performance, fewer bottleneck scenarios, and smoother gameplay.
What Causes a CPU Bottleneck?
CPU bottlenecks happen for a bunch of reasons—both hardware and software make a difference.
✅ Old CPU with powerful GPU: Causes of CPU bottleneck usually start when I pair a weak processor with a strong graphics card.
✅ Too many background processes: Apps running in the background eat up CPU power.
✅ Low core/thread count: Fewer cores or threads means the CPU can’t handle heavy tasks.
✅ Poor cooling (thermal throttling): Overheating slows the CPU down.
✅ Misconfigured settings: Bad BIOS or power plans can hurt CPU performance.
Quick tip: I check Task Manager to spot background processes that hog CPU. Keeping BIOS and drivers updated helps stop some CPU GPU imbalance and thermal throttling, too.
Benchmark Insights: 6-Core vs 8-Core CPU Performance
Benchmarks show me the real impact of CPU core count on gaming performance and multitasking. Here’s a quick look at some benchmark results for popular games and tasks (data from TechPowerUp):
| Game/Application | 6-Core FPS | 8-Core FPS | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyberpunk 2077 | 72 | 85 | +13 FPS |
| Call of Duty: MWIII | 110 | 123 | +13 FPS |
| Adobe Premiere (Render) | 180s | 142s | 38s faster |
| Red Dead Redemption 2 | 80 | 95 | +15 FPS |
I notice the FPS difference grows in CPU-heavy games and when I’m multitasking. Extra cores really help in open-world games, streaming, and video editing.
Real User Fixes & Community-Backed Solutions
I found a detailed discussion on Quora where users broke down what a CPU bottleneck is and why it’s so common in gaming. A CPU bottleneck happens when your processor can’t keep up with your graphics card, meaning the CPU can’t deliver data fast enough for the GPU to work at full speed.
As a result, your system’s performance is held back not by the power of your graphics card, but by the CPU’s ability to handle things like game logic, AI, physics, and other behind-the-scenes tasks.
This bottleneck is common in gaming for a few reasons. Modern games often require the CPU to process a lot of information every frame, especially in open-world or simulation games with many objects, NPCs, or events.
If you pair a fast GPU with a weaker CPU, the GPU ends up waiting on the CPU, leading to lower frame rates, stuttering, or even freezing. It’s especially noticeable at lower resolutions (like 1080p), where the GPU can finish its work quickly and is left waiting for the CPU. That’s why balancing your CPU and GPU is important for smooth gameplay—your game can only run as fast as your slowest component allows.
In another Quora discussion, I found that a CPU bottleneck happens when your processor (CPU) can’t keep up with the demands of other components, usually the graphics card (GPU).
Imagine playing a game where your CPU is maxed out at 100% usage but your GPU is only at 60%. This means the CPU is working as fast as it can, but it can’t send enough instructions to the GPU, so the GPU is held back and can’t perform at its best.
This situation is common in gaming, especially when pairing a strong graphics card with an entry-level or older CPU. Modern games often ask the CPU to handle lots of tasks beyond graphics, such as AI, physics, world logic, and networking.
If your CPU can’t process all this quickly, it slows everything down, leading to lower frame rates, stutters, or lag, even if your GPU is very powerful.
Final Verdict
A CPU bottleneck happens when your processor can’t keep up with your graphics card or other system parts, causing slowdowns, low FPS, and stutter, even with a high-end GPU. It’s especially common in gaming, where the CPU has to handle game logic, AI, and background tasks every frame. When your CPU is maxed out but your GPU isn’t, you’re not getting the performance you paid for.
The best fix is to balance your hardware: pair your GPU with a CPU that matches its power, keep your drivers and BIOS up to date, and close unnecessary background apps. Use monitoring tools to spot bottlenecks early. If your CPU is always at 100% while gaming, upgrading to a faster processor with more cores is the most effective way to boost overall performance and enjoy smoother, lag-free gameplay.
FAQ’s
How to determine if a CPU is bottlenecking?
I usually check for CPU bottlenecking by watching CPU and GPU usage during a graphics-intensive application. If I see CPU usage near 100% while GPU usage stays much lower, it tells me the CPU is the bottleneck. This way, I know which part holds my system back.
Is 100% CPU usage a bottleneck?
100% CPU usage doesn’t always mean there’s a bottleneck. Sometimes, the CPU just has a heavy processing load, like busy servers running lots of tasks. If high usage keeps happening, I might need a CPU upgrade to keep things smooth.
Will bottleneck damage CPU?
A bottleneck won’t damage my CPU or GPU. It just means one part limits how well the other works. My hardware stays safe, but system efficiency drops because of the performance limiting. There’s no risk to the hardware itself.
Is a 7% bottleneck ok?
I’d say the ideal bottleneck is 0%, but I don’t worry much if it’s under 5%. A 7% bottleneck is still okay for most people. If I see single-digit percentages, I just do a bit more research before changing my setup.
When will cpu bottleneck gpu?
A CPU bottlenecks a GPU when it can’t process data fast enough for the graphics card. This usually happens in CPU-heavy tasks, like open-world games, where the CPU needs to handle lots of things at once. Using a low-end CPU with a high-end GPU causes this a lot.
Can cpu bottleneck cause crashes?
A CPU bottleneck alone doesn’t usually cause crashes. When my CPU is maxed out, I notice more stuttering, freezes, or system instability. Actual crashes mostly happen if there’s overheating or another hardware or software problem on top of the bottleneck. So, bottlenecks make things choppy, not broken.

