I’ve tested this a lot, and refresh rate changes more than people think. A refresh rate test shows how monitor Hz directly affects smooth gameplay and FPS stability. If frames are unstable, even high FPS feels bad.
From 60Hz to 360Hz, the difference is not small. 60Hz shows 16.67ms per frame. 144Hz drops to 6.94ms. 240Hz runs at 4.16ms. And 360Hz pushes down to 2.78ms. Lower frame time means faster updates. But it also means your system must deliver stable frames every single cycle.
Higher monitor Hz increases CPU load because frame pacing becomes tighter. Any CPU bottleneck shows up fast at 240Hz and above. And RAM latency starts to affect 1% low FPS more clearly. Smoothness is not just average FPS. It is frame time consistency.
In high refresh gaming, esports titles like Valorant and CS2 often exceed 300 FPS on tuned systems. That makes 240Hz to 360Hz realistic when CPU-bound. Research on motion clarity also shows visible improvement from 60Hz to 120Hz and higher, especially during fast camera movement.

Performance depends on:
- FPS stability
- 1% low FPS
- Frame pacing consistency
- Input latency control
And if you're building a high-performance system for gaming or content creation, our RAID Calculator can help estimate storage capacity and performance when using multiple drives. That is where real gaming performance comes from. For more PC performance tools and system analysis resources, visit our homepage at Bottleneck Calculator Online.
How To Use Refresh Rate Test Video
Understanding Monitor Refresh Rate in Gaming Performance
Refresh rate in gaming affects how smooth movement looks, not just how high the FPS counter goes. A monitor updates the image many times per second, and that update speed changes how motion feels. Even if two systems show the same FPS, the one with higher monitor Hz often looks cleaner and more stable. Smooth gameplay depends on motion clarity and frame pacing, not only raw frame numbers.
If you want to estimate your real-world performance before upgrading, you can use our FPS Calculator to check expected frame rates based on your CPU and GPU. That is why FPS vs refresh rate is not the same thing. The display refresh cycle shapes how performance is perceived.
What Is Refresh Rate (Hz)?
Monitor Hz meaning is simple. It shows how many times the screen updates every second. If a display runs at 144Hz, it refreshes 144 times per second. As defined by VESA display standards, refresh rate measures display refresh cycles per second under standardized timing rules.
A monitor cannot show more frames than its refresh rate. If you have a 240Hz gaming display, it can show up to 240 frames per second.
Here is how frame time changes:
60Hz = 16.67ms
144Hz = 6.94ms
240Hz = 4.16ms
360Hz = 2.78ms
Lower frame time improves motion clarity and reduces perceived blur caused by sample and hold behavior in LCD panels. According to NVIDIA’s official FPS and refresh rate guide, higher refresh rates make motion appear clearer and improve responsiveness in fast games. That is why 60Hz vs 144Hz looks very different in shooters.
120Hz also became mainstream during the HDMI 2.1 era around the PS5 and Xbox Series X launch, which pushed refresh rate awareness into console gaming too.
Refresh Rate vs Resolution
Monitor resolution vs refresh rate often gets mixed up. If you're adjusting internal render resolution for performance balance, try our Resolution Scaling Calculator to quickly compute scaled output values. They do different things.
Resolution means pixel count like 1080p, 1440p, or 4K.
Refresh rate means how often the image updates each second.
RTINGS laboratory testing explains that refresh rate influences motion clarity while resolution determines image detail.
Key differences:
- Resolution increases sharpness and visual detail, and if you want to calculate how sharp your display actually is, you can use our Pixel Density Calculator to measure exact PPI.
- Refresh rate increases motion smoothness
- Higher resolution increases GPU load
- Higher refresh rate increases CPU and frame pacing demand
A 360Hz monitor does not add more detail. It updates motion faster. And that difference matters in fast camera movement and competitive play.
FPS vs Refresh Rate — How System Output Interacts with Display Limits
FPS vs refresh rate is where most performance confusion starts. FPS is how many frames the GPU renders every second. Refresh rate is how many frames the display can physically show. Smooth gameplay depends on how well those two stay in sync. If system output and monitor timing mismatch, you get stutter in gaming, tearing, or wasted performance. Frame pacing matters just as much as average FPS. A stable system always feels smoother than one with fluctuating output.
What Happens When FPS Is Lower Than Refresh Rate?
When FPS is lower than refresh rate, the monitor repeats frames. A 144Hz display refreshing every 6.94ms cannot invent new frames if the GPU delivers them late. That creates uneven motion.
On a 144Hz monitor running at unstable 90–110 FPS, you often notice:
- Visible stutter in gaming
- Frame pacing inconsistency
- Higher impact from 1% low FPS drops
- Underused display refresh capability
Blur Busters explains that frame pacing inconsistencies create visible stutter even when average FPS seems high. That is why stable 140 FPS feels smoother than unstable 160 FPS with bad 1% lows.
What Happens When FPS Exceeds Refresh Rate?
When FPS is higher than refresh rate, the display refresh cap limits visible motion updates. A 144Hz panel cannot show more than 144 unique frames per second.
But higher FPS still matters.
- Extra frames reduce render queue delay
- System latency decreases
- Input latency improves even above refresh cap
For example, 300 FPS on a 144Hz monitor can produce lower system latency than locking at 144 FPS. NVIDIA’s latency research shows that higher system FPS reduces overall system latency, even when exceeding monitor refresh rate. This is why competitive players often chase high FPS numbers.
Using V Sync caps FPS to refresh rate, which removes tearing, but it can increase input lag due to buffering.
Effective Displayed FPS Explained
Effective FPS means the maximum visible updates allowed by the display refresh cap.
If a system outputs 400 FPS on a 240Hz monitor:
Max visible motion updates = 240 per second
Frame time = 4.16ms
Visible smoothness stops at 240Hz. But latency can still improve because newer frames enter the pipeline faster.
So visible smoothness and system latency are not the same thing. And understanding that difference is key to real gaming performance.
Refresh Rate Benchmark Test — CPU Bound Performance Analysis
This refresh rate benchmark focuses on CPU bound gaming to isolate true refresh rate scaling. GPU bottlenecks can hide real behavior at high Hz. When the graphics card limits performance, you cannot see how frame pacing reacts to tighter frame time budgets. Competitive games often become CPU limited at low settings, especially titles like CS2, Valorant, and Fortnite where players reduce visuals for FPS stability. Testing in a CPU bound scenario reveals how refresh rate scaling stresses scheduling precision and memory latency.
Test Setup and Methodology
The goal was to remove GPU limitations and expose high refresh performance behavior.
Hardware configuration:
- High end GPU to eliminate GPU bottleneck
- Modern 8 core high clock CPU class
- 16 to 32GB dual channel RAM
- 1080p resolution
- Low graphics settings
- V Sync off
- VRR off
Low settings shift workload toward the CPU. That makes refresh rate scaling easier to observe. Testing was evaluated at fixed tiers: 60Hz, 144Hz, 240Hz, and 360Hz.
Performance Scaling at 60Hz, 144Hz, 240Hz, and 360Hz
As refresh rate increases, the frame time budget shrinks. That makes CPU scheduling and RAM latency more critical.
Refresh Rate | Frame Time | Stability Requirement
60Hz | 16.67ms | Low
144Hz | 6.94ms | Moderate
240Hz | 4.16ms | High
360Hz | 2.78ms | Very High
At 60Hz, sustaining 60 FPS is relatively easy. CPU stress remains low.
At 144Hz, smoothness improves noticeably. Stable 144 FPS becomes necessary for consistent frame pacing.
At 240Hz, the 4.16ms frame window tightens. A 240Hz CPU bottleneck becomes visible if scheduling wavers.
At 360Hz, the 2.78ms frame time budget leaves almost no margin. Even a 1ms delay consumes over 35 percent of the total frame window. That sensitivity explains why 360Hz performance requirements demand extremely stable CPU bound gaming behavior.
Why 1% Low FPS Becomes Critical at High Refresh Rates
1% low FPS measures the average of the worst performing 1 percent of frames. At 60Hz, small drops may go unnoticed. But at 240Hz and above, the frame time window becomes extremely tight. 240Hz allows only 4.16ms per frame. 360Hz allows just 2.78ms. In that small window, even minor instability becomes visible. High refresh gaming does not reward peak FPS spikes. It rewards frame consistency. Smoothness at 240Hz gaming stability depends on how steady frame delivery stays under load.
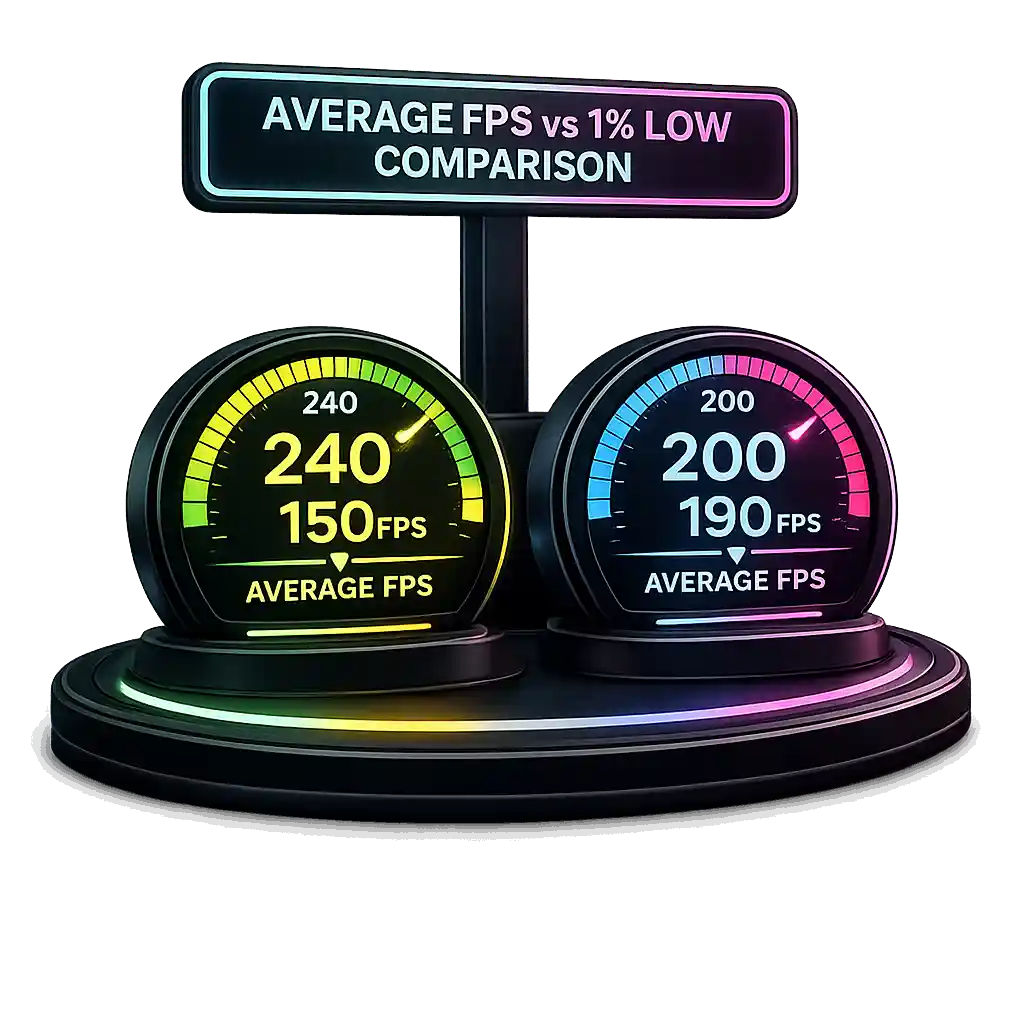
Average FPS vs 1% Low Comparison
Average FPS shows overall performance. 1% low FPS shows how bad performance gets during heavy moments.
Consider this comparison:
• 240 FPS average with 150 FPS 1% low
• 200 FPS average with 190 FPS 1% low
On a 240Hz display, the second setup feels smoother. The first has large variance. That variance causes micro stutter during tracking or fast flick shots. Intel notes that frame consistency matters more than peak FPS when optimizing gaming performance. In competitive play, stable output improves aim reliability and reaction timing.
Frame Time Consistency at High Hz
Frame time spikes explain why instability feels worse at high refresh.
240 FPS = 4.16ms per frame
Drop to 120 FPS = 8.33ms
That doubles the frame time instantly. The jump creates visible hitching.
At 360Hz smoothness levels, a 2ms spike nearly doubles the 2.78ms frame window. High refresh exposes even small inconsistencies.
Hardware factors that affect frame pacing:
• CPU scheduling precision
• RAM latency gaming performance
• Background processes
• Thermal throttling
Lower RAM latency improves frame delivery timing. If you're optimizing for competitive gaming, you can calculate your true memory response time using our RAM Latency Calculator to see how timings impact 1% lows. Stable CPU core behavior reduces spikes. That is why esports players often cap FPS slightly above refresh rate, such as 250 FPS on 240Hz, to control variance and maintain consistent frame pacing.
CPU and RAM Requirements for High Refresh Rate Gaming
Higher refresh rate means a smaller frame time budget. At 240Hz, each frame must complete in 4.16ms. At 360Hz, the window drops to 2.78ms. That small window increases CPU scheduling pressure. Sustaining ultra-high refresh gaming also increases total system power demand, especially when paired with high-end GPUs, so it’s worth checking your PSU headroom using our PSU Wattage Calculator before upgrading, and you can estimate long-term energy usage with our Electricity Cost Calculator.
Memory timing also affects frame delivery. At 60Hz, the GPU often limits performance. But in high refresh rate CPU requirement scenarios, especially at 240Hz and above, the processor and RAM become the primary constraints. Frame time consistency becomes harder to maintain as the margin for delay shrinks.
CPU Bottlenecks at 240Hz and Above
The CPU handles game logic, physics, AI, and draw calls. In 240Hz CPU bottleneck situations, the processor must finish its workload inside 4.16ms. At 360Hz CPU performance levels, it must complete everything within 2.78ms. If it exceeds that window, a frame drop occurs.
Weak CPUs struggle due to:
- Low single-core performance
- Unstable boost clocks
- Limited cores for background tasks
- Thermal throttling
A CPU capable of sustaining 120 to 160 FPS may fail to hold consistent 240 FPS. That causes sharp 1% low drops. In esports titles like CS2 and Valorant, which are highly CPU dependent at low settings, single-thread performance matters more than total core count. Background processes such as recording software or open browser tabs increase CPU scheduling variance and hurt stability.
RAM Latency Influence on Frame Stability
RAM latency gaming performance affects how quickly the CPU retrieves data. CAS latency impact determines responsiveness, while frequency controls bandwidth.
Frequency in MHz increases data throughput.
Latency in CL timing affects access delay.
Lower memory timing gaming values improve frame time consistency. Reducing latency by even 5 to 10ns can stabilize 1% lows in CPU bound titles. At 360Hz, even sub millisecond delays become visible as micro stutter. High frequency combined with low latency delivers more stable frame pacing under CPU scheduling gaming loads.
Refresh Rate and Input Latency in Gaming
Input lag is the time between your action and the moment it appears on screen. When you click a mouse or press a key, the system processes the input, renders the frame, and then the display shows it. Refresh rate input lag is directly connected because the screen can only update during its next refresh cycle. Higher monitor Hz means shorter frame intervals and faster visual feedback. It does not remove total system latency, since CPU and GPU render time still matter, but it reduces display latency gaming significantly.
Frame Time per Refresh Rate (ms Breakdown)
Each refresh rate equals a specific frame time ms value. That frame time defines the maximum display update delay.
Refresh Rate | Frame Time per Refresh
60Hz | 16.67 ms
144Hz | 6.94 ms
240Hz | 4.16 ms
360Hz | 2.78 ms
At 60Hz, worst case display delay can reach 16.67ms before the next update. At 240Hz latency levels, that delay drops to 4.16ms. At 360Hz response time levels, it falls to 2.78ms. Higher refresh reduces scanout time because the display updates more frequently from top to bottom. That directly lowers perceived latency.
Still, total delay depends on CPU and GPU processing speed. Display refresh is one part of the latency chain.
Competitive Advantage of High Refresh Rates
High refresh esports monitors improve monitor Hz responsiveness in fast scenarios. Faster updates provide clearer motion and quicker visual confirmation.
Benefits include:
• Improved target tracking
• Better flick accuracy
• Faster reaction time gaming response
• Clearer motion during rapid camera movement
Reduced motion blur improves player perception during fast tracking. Professional tournaments widely adopted 240Hz competitive gaming monitors between 2017 and 2019. 360Hz entered competitive scenes after 2020.
For casual players, gains beyond 240Hz show diminishing returns. But in high refresh esports environments, lower display latency gaming provides measurable competitive advantage.
When a Higher Refresh Rate Doesn’t Improve Gaming Performance
A higher refresh rate does not automatically improve gaming performance. Gains depend on where the system bottleneck exists. If the workload is CPU bound, higher Hz can improve responsiveness. If the workload is GPU bound, refresh upgrades may show no benefit. CPU vs GPU bottleneck balance determines whether high refresh scaling is possible. Upgrade decisions must match resolution, settings, and game type rather than assuming more Hz always equals better results.
GPU-Bound Gaming at Higher Resolutions
GPU bound gaming occurs when the graphics card limits frame production. At 1440p and especially 4K gaming performance levels, pixel count rises sharply. 4K resolution renders 3840×2160 pixels, over 8.29 million per frame. 1080p renders 2.07 million. That is a fourfold increase in shading, rendering, and memory bandwidth demand.
1080p low settings often become CPU bound.
4K ultra settings typically become GPU bound.
TechSpot benchmark analysis shows that as resolution increases to 4K, performance scaling becomes heavily GPU limited, reducing CPU impact. If a GPU produces 80 to 120 FPS at 4K, upgrading from 144Hz to 240Hz provides no visible improvement. Ray tracing increases GPU load further, tightening limits.
Casual and Story-Driven Games
Casual gaming refresh rate needs differ from esports. Story driven games FPS targets often sit between 60 and 120 FPS. These titles prioritize visual fidelity, lighting, and immersion over ultra high frame pacing.
Competitive shooters benefit most from fast camera movement and rapid tracking. Slower RPGs, strategy titles, or cinematic games show minimal difference between 144Hz vs 240Hz 4K. High refresh helps most where motion intensity is high. In narrative focused gameplay, the impact becomes context dependent rather than essential.
How to Choose the Right Refresh Rate for Your Gaming Setup
The best refresh rate for gaming depends on three things: what you play, how many FPS you can hold, and what your hardware can sustain. Bigger numbers are not always better. Diminishing returns start to appear as refresh rates climb. Performance consistency matters more than marketing labels. If your system cannot deliver stable frames, a higher Hz panel will not fix instability. Match the monitor to your real FPS output, not your peak numbers.
Best Refresh Rate for Casual Gaming
For casual gaming refresh rate needs, 60Hz is still an acceptable baseline. But 120Hz or 144Hz offers a clear upgrade without extreme hardware demand.
Why 144Hz works well:
- Large smoothness jump from 60Hz
- Easier to sustain than 240Hz+
- Balanced CPU and GPU requirements
- Works well for story driven games and RPGs
144Hz is widely viewed as the value sweet spot for PC users. Consoles like PS5 and Xbox Series X support up to 120Hz through HDMI 2.1, making 120–144Hz practical for mixed use.
Best Refresh Rate for Competitive Gaming
For a competitive gaming monitor, tiers matter.
144Hz
Entry competitive level
Easy to maintain stable FPS
240Hz
4.16ms frame window
Common in esports tournaments
Requires strong CPU and optimized settings
360Hz monitor gaming
2.78ms frame window
For high-level competitive players
Demands top-tier CPU stability
The jump from 60 to 144Hz is large.
144 to 240Hz is noticeable for serious players.
240 to 360Hz offers smaller but measurable gains.
Many esports events standardized around 240Hz, making it a competitive baseline today.
Can Your PC Handle 240Hz or 360Hz?
Before asking if 240Hz is worth it, check your system.
- Can you sustain target FPS consistently?
- Are 1% lows within 10–15% of average FPS?
- Is single-core performance strong?
- Is RAM latency optimized?
- Are background processes minimized?
If average FPS is 300 but 1% lows drop to 180, 240Hz will not feel stable. At 240Hz you have 4.16ms per frame. At 360Hz only 2.78ms. That margin is small.
If your system cannot maintain at least 85–90% of the monitor refresh rate in stable FPS, upgrading may not deliver full benefit. Always benchmark your real in-game performance before deciding.
Why Your 165Hz Monitor Is Locked at 120Hz and How to Fix It
This is a common problem. Your monitor supports 165Hz, but your system shows only 120Hz. The panel is not broken. Usually, something is limiting it. It could be the cable, the port, Windows settings, or GPU configuration. Sometimes the monitor itself ships in 120Hz or 144Hz mode by default. The good news is this is usually fixable in a few minutes.
Common Causes
- HDMI 1.4 cable causing HDMI 120Hz limit
- Using HDMI instead of DisplayPort 165Hz connection
- Windows change refresh rate not set to 165Hz
- NVIDIA change refresh rate not configured
- GPU bandwidth limitation
- Laptop output port capped at 120Hz
- Monitor overclock mode not enabled in OSD
HDMI 2.0 supports higher refresh rates at 1080p, while HDMI 1.4 often caps at 120Hz. That is a common reason a 165Hz monitor gets stuck at 120Hz.

How to Fix It
- Check your cable
Use DisplayPort 1.2 or higher. Or HDMI 2.0+. Avoid older HDMI cables. - Change refresh rate in Windows
Settings → Display → Advanced Display → Select 165Hz. - Check GPU control panel
NVIDIA Control Panel → Change Resolution → Select 165Hz.
AMD Radeon Settings → Display → Refresh Rate. - Enable monitor overclock mode
Some 165Hz panels ship at 144Hz by default. Turn on 165Hz inside the monitor OSD. - Update GPU drivers
Old drivers can limit available refresh options. - Test a different cable or port
If still locked at 120Hz, swap cable or use another GPU port.
165Hz at 1080p needs more bandwidth than 120Hz. If the cable or port cannot handle it, the system will cap it automatically. In most cases, switching to DisplayPort fixes the issue fast.
Does HDMI 2.0 Really Support 165Hz at 1080p?
Yes. HDMI 2.0 165Hz at 1080p works in most cases. The key factor is bandwidth. Support depends on the GPU, the monitor’s HDMI port, cable quality, and color format settings. If all components meet spec, 1080p 165Hz HDMI runs without issue. Problems usually happen when older HDMI versions or low-quality cables are used.
According to the official HDMI 2.0 specification published by the HDMI Forum, HDMI 2.0 supports up to 18 Gbps of bandwidth. 1920×1080 at 165Hz fits within that limit using standard 8-bit RGB. Higher color depth like 10-bit increases bandwidth demand. Enabling HDR can reduce maximum refresh capability. Using 8-bit color improves compatibility at high refresh rates.
Comparison
HDMI 1.4
10.2 Gbps
Typically supports 1080p up to 120Hz
HDMI 2.0
18 Gbps
Supports 1080p 144Hz and 165Hz
DisplayPort 1.2
21.6 Gbps
More reliable for high refresh PC gaming
Some monitors default to 144Hz over HDMI unless changed manually. Long or poor-quality cables can also force fallback to 120Hz. For consistent high refresh PC gaming, DisplayPort remains the safer choice.
HDMI vs DisplayPort for 144Hz and 165Hz Gaming, Which Should You Use?
Both HDMI and DisplayPort can handle 144Hz HDMI support and 165Hz DisplayPort at 1080p. The difference comes down to version and stability. HDMI 1.4, HDMI 2.0, DisplayPort 1.2, and 1.4 all offer different bandwidth limits. For PC gaming, bandwidth headroom and adaptive sync support usually decide the better gaming monitor cable choice.
Technical Comparison
HDMI 1.4
10.2 Gbps
Typically supports 1080p up to 120Hz
HDMI 2.0
18 Gbps
Supports 1080p 144Hz and 165Hz
DisplayPort 1.2
21.6 Gbps
Supports 1080p 165Hz easily
Supports 1440p 144Hz reliably
DisplayPort 1.4
32.4 Gbps
Better for high resolution and high refresh combinations

Gaming Differences
DisplayPort advantages:
- Higher bandwidth headroom
- More consistent high refresh PC support
- Strong early support for G Sync and FreeSync
- Daisy chaining support
HDMI advantages:
• Standard for TVs and consoles
• HDMI 2.1 required for 4K 120Hz on PS5 and Xbox Series X
Adaptive sync technologies first launched over DisplayPort before expanding to HDMI, which is why DP remains common in high refresh PC setups.
Recommendation
For PC gaming at 144Hz or 165Hz, DisplayPort is generally preferred. It offers more stable high refresh behavior. For consoles, HDMI 2.1 is required for 120Hz. Avoid HDMI 1.4 for 165Hz. Always use certified cables to prevent signal drop issues.
Do You Actually Need DisplayPort 1.4 for 165Hz Gaming?
No. DisplayPort 1.4 is not required for 165Hz at 1080p. DisplayPort 1.2 is already sufficient for that refresh rate. The version you need depends on resolution and refresh combined, not just the Hz number. For standard 1080p 165Hz gaming, newer standards are not mandatory.
Per VESA DisplayPort documentation, DisplayPort 1.2 provides 21.6 Gbps of bandwidth, while DisplayPort 1.4 increases total bandwidth to 32.4 Gbps. 1080p at 165Hz fits comfortably within DP 1.2 limits. Even 1440p 165Hz DisplayPort setups usually work on DP 1.2 without issue.
DisplayPort 1.2
21.6 Gbps
Supports 1080p 165Hz
Supports 1440p 144–165Hz
DisplayPort 1.4
32.4 Gbps
Better for 4K 120Hz+
Handles HDR and higher color depth more comfortably
DP 1.4 becomes relevant mainly for 4K high refresh or HDR gaming. Many GPUs since 2014–2016 already support DP 1.2 or higher, so 165Hz gaming cable compatibility is widespread. Just remember to enable 165Hz in the monitor OSD if required.
How to Enable 165Hz in Windows Display Settings (Step by Step Guide)
Sometimes Windows sets your monitor to 60Hz or 120Hz by default. Even if your display supports 165Hz, you still need to select it manually. If your monitor and cable support it, enabling 165Hz takes less than a minute. If your monitor is stuck at 60Hz or 120Hz, this usually fixes it fast.
Windows 11
- Right click Desktop → Click Display Settings
- Click Advanced Display
- Select the correct monitor (if you use multiple displays)
- Under Choose a refresh rate, select 165Hz
- Click Apply
Windows 10
- Right click Desktop → Click Display Settings
- Scroll down → Click Advanced Display Settings
- Click Display Adapter Properties
- Open the Monitor tab
- Choose 165Hz from the Screen Refresh Rate dropdown
- Click Apply
The screen may flicker briefly. That is normal when switching refresh rates.
If 165Hz Is Not Showing
- Check cable type (HDMI 2.0+ or DisplayPort 1.2+)
- Update GPU drivers
- Check NVIDIA or AMD control panel refresh rate
- Enable monitor overclock mode in the OSD
- Make sure correct resolution is selected
Windows only shows refresh rates supported by your GPU output, cable bandwidth, and monitor profile. If bandwidth is limited, the 165Hz option will not appear. If using multiple monitors, GPU bandwidth sharing can also limit available refresh rates.
How to Change Refresh Rate in NVIDIA Control Panel (Step by Step)
Sometimes Windows does not show all refresh rate options. That is where NVIDIA Control Panel helps. It lets you change refresh rate at the GPU level. If 165Hz not showing in Windows, or 144Hz / 240Hz missing, this method often unlocks it.
Step by Step Guide
- Right click Desktop → Open NVIDIA Control Panel
- Go to Display → Change Resolution
- Select the correct monitor (if using multiple displays)
- Under the PC section, choose your native resolution (example: 1920×1080)
- In the Refresh Rate dropdown, select 165Hz
- Click Apply
Important: Always choose resolution under the PC category, not “Ultra HD, HD, SD.” The wrong category can limit refresh rate due to chroma subsampling.
If 165Hz Is Not Showing
- Use DisplayPort or HDMI 2.0+
- Update NVIDIA drivers
- Enable 165Hz or overclock mode in monitor OSD
- Confirm monitor supports 165Hz at current resolution
- Try creating a custom refresh rate NVIDIA profile
To create one:
Go to Customize → Create Custom Resolution → Enter 165Hz → Test → Save
Some laptops using Optimus may limit refresh rate if the display routes through integrated graphics.
NVIDIA Control Panel directly controls GPU output timing. If refresh is limited here, the issue is usually cable bandwidth, monitor firmware, or GPU port version.
How to Safely Create a Custom 144Hz or 165Hz Resolution
You usually create a custom refresh rate when 144Hz not showing or 165Hz not appearing in settings. Sometimes this involves light monitor overclock 165Hz behavior. Most modern gaming monitors already support 144Hz or 165Hz natively, so this is often just unlocking it. Still, you should test carefully. A safe monitor overclock means small changes and stability checks.
NVIDIA Custom Resolution Steps
- Right click Desktop → Open NVIDIA Control Panel
- Go to Display → Change Resolution
- Click Customize
- Select Create Custom Resolution
- Keep native resolution (example: 1920×1080)
- Change refresh rate to 144Hz or 165Hz
- Click Test
- If stable, click Yes to save
AMD (Brief)
Open Radeon Software → Go to Display → Create Custom Resolution → Enter refresh rate → Test and apply.
Safety Precautions
- Increase refresh slightly, not extreme jumps
- Use quality DisplayPort or HDMI 2.0+ cable
- Do not change timing parameters unless experienced
- If screen turns black, wait 15 seconds for auto revert
- Watch for flickering, artifacting, or signal loss
Higher refresh raises pixel clock demand. If bandwidth exceeds cable or panel limits, instability happens. You may see frame skipping or image corruption. Rarely, extreme overclocking can reduce panel lifespan.
Many monitors advertise 165Hz as factory validated overclock in the OSD. That is safer than manual edits. If custom refresh works, run a frame skipping test tool before long-term use to confirm stability.
Why Custom Refresh Rates Can Cause Screen Tearing or Visual Artifacts
Custom refresh rates push the monitor beyond its default timing profile. When you increase Hz manually, you also increase signal demand. If something in the chain cannot handle it, instability shows up. That is when users notice custom refresh rate artifacts or screen tearing 165Hz issues. Most of the time, this is caused by bandwidth limits, timing misconfiguration, or sync mismatch. The good part is that it is usually reversible.
Increasing refresh rate raises pixel clock demand. Higher Hz also shrinks the frame-time window.
144Hz = 6.94ms
165Hz = 6.06ms
240Hz = 4.16ms
Since refresh rate directly controls frame timing, similar time-to-frame conversions are also used in video production — you can calculate exact frame totals using our Timecode to Frame Converter when working with precise timelines.
If the GPU cannot deliver frames consistently, tearing appears. Tearing happens when two frames display at once because FPS and refresh rate are not synchronized. Without VRR, mismatched FPS and Hz increase tearing risk.
Artifacts are different. They usually mean signal instability. If HDMI bandwidth issue or cable limits are reached, corruption appears. Even a small timing miscalculation in custom resolution can destabilize signal transmission. If artifacts appear immediately after increasing refresh rate, it often indicates bandwidth limitation rather than GPU performance.
Common Causes
- HDMI 1.4 bandwidth limitation
- Low quality or long cables
- Incorrect custom timing parameters
- Monitor overclock artifacts
- VRR disabled during unstable FPS
- GPU unable to sustain target FPS
How to Fix It
- Revert to native refresh rate
- Enable G Sync tearing fix or FreeSync
- Use DisplayPort for better stability
- Lower custom refresh slightly (165 → 160Hz)
- Avoid manual timing edits
Most refresh rate instability issues disappear once you return to validated settings.
Frame Time Comparison Table — Refresh Rate vs Stability Requirements
This table shows how refresh rate directly reduces frame time and increases performance demand. As Hz increases, the frame-time window shrinks. That makes FPS stability and frame pacing more critical.
| Refresh Rate | Frame Time per Frame (ms) | Required Stable FPS | Frame-Time Budget Strictness | CPU Scheduling Sensitivity | Noticeable Stutter Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60Hz | 16.67 ms | 60 FPS | Low | Low | Low |
| 120Hz | 8.33 ms | 120 FPS | Moderate | Moderate | Low–Medium |
| 144Hz | 6.94 ms | 144 FPS | Moderate–High | Increased | Medium |
| 165Hz | 6.06 ms | 165 FPS | High | High | Medium–High |
| 240Hz | 4.16 ms | 240 FPS | Very High | Very High | High if unstable |
| 360Hz | 2.78 ms | 360 FPS | Extreme | Extremely High | Very High |
Motion Blur Persistence — MPRT vs GtG vs Refresh Rate
Higher Hz does not automatically mean perfect motion clarity. Many people assume a 360Hz panel removes blur completely. That is not how display behavior works. Motion blur depends on refresh rate, pixel response time, and how the screen holds each frame.
Sample and Hold Displays
Most modern LCD monitors use sample and hold behavior. That means each frame stays visible on screen until the next refresh. Your eyes track moving objects while the image remains static between updates. That creates perceived motion blur, even if pixel response is fast.
Higher refresh rate reduces how long each frame stays visible. But it does not eliminate persistence blur entirely.
MPRT vs GtG vs Hz
GtG (Gray to Gray) measures how fast pixels change color.
MPRT (Moving Picture Response Time) measures visible motion persistence.
Refresh rate controls how often frames update.
Even if GtG is low, sample and hold blur can remain. For example:
144Hz = 6.94ms frame visibility
240Hz = 4.16ms
360Hz = 2.78ms
Shorter frame visibility reduces blur, but only proportionally.
Why 360Hz Doesn’t Automatically Mean Clear Motion
360Hz lowers frame persistence to 2.78ms. That improves clarity compared to 144Hz. But blur can still appear if:
• Frame rate is unstable
• Pixel transitions are slow
• Backlight strobing is not used
Motion clarity depends on the combination of refresh rate, pixel response, and frame consistency. Higher Hz helps, but it is only one part of motion performance.
G Sync vs FreeSync vs Fixed Refresh Rate
At 240Hz, the frame window is only 4.16ms. If FPS fluctuates, even small drops become visible. With fixed refresh rate, the monitor refreshes on schedule no matter what the GPU does. If FPS changes, you get screen tearing or micro stutter.
When FPS moves between 180 and 240 on a fixed 240Hz panel, frame pacing breaks. Parts of two frames can appear at once. That is tearing. Or frames repeat unevenly. That is stutter.
G Sync and FreeSync use VRR. The monitor adjusts its refresh timing to match GPU output. If FPS drops to 198, the panel refreshes at 198Hz. That keeps frame delivery aligned.
Unlike V Sync, VRR does not force the GPU to wait for the next refresh cycle. So it avoids the extra input latency penalty.
High Hz without VRR still improves smoothness. But when FPS is unstable, fixed refresh cannot hide timing variance. VRR keeps motion consistent without adding delay.
FAQs
Is there a way to test refresh rate?
Yes. You can test refresh rate in a few simple ways:
• Go to Windows Display Settings → Advanced Display to see current Hz
• Use online motion test tools like UFO frame rate tests
• Check your GPU control panel (NVIDIA or AMD)
If motion looks smooth and the test shows the correct Hz, it is working. For deeper checks, frame skipping test tools can verify stability.
Is there a 1000Hz monitor?
No consumer 1000Hz monitor exists yet. Research prototypes have demonstrated ultra high refresh displays, but mainstream gaming monitors currently reach up to 360Hz or 500Hz in select esports models. 1000Hz requires extreme bandwidth and panel response improvements.
Does 240 Hz mean 240 FPS?
No. 240Hz means the monitor can display up to 240 frames per second. Your GPU must actually generate 240 FPS. If your system only produces 160 FPS, the monitor will not magically create more frames.
Is 60Hz vs 144Hz noticeable?
Yes, very noticeable. 60Hz updates every 16.67ms.
144Hz updates every 6.94ms.
That large reduction in frame time improves motion clarity and input responsiveness, especially in fast games.
Can the human eye see the difference between 60Hz and 120Hz?
Yes. Research in visual perception shows motion clarity improves beyond 60Hz, especially during fast movement. Many users clearly detect smoother motion at 120Hz and above.
Why does 60 FPS feel choppy on 144Hz?
Because the monitor refreshes every 6.94ms but the GPU only delivers a new frame every 16.67ms. Frames repeat unevenly, causing frame pacing mismatch. Without VRR, this mismatch makes 60 FPS feel less smooth on a 144Hz display.

